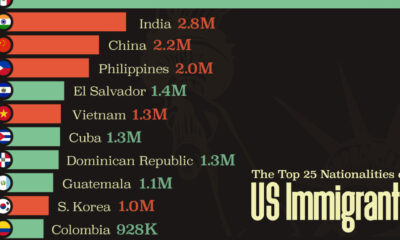
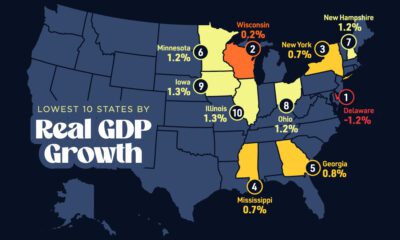
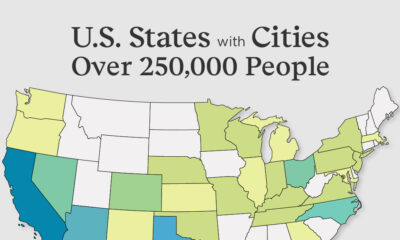
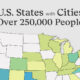
Money
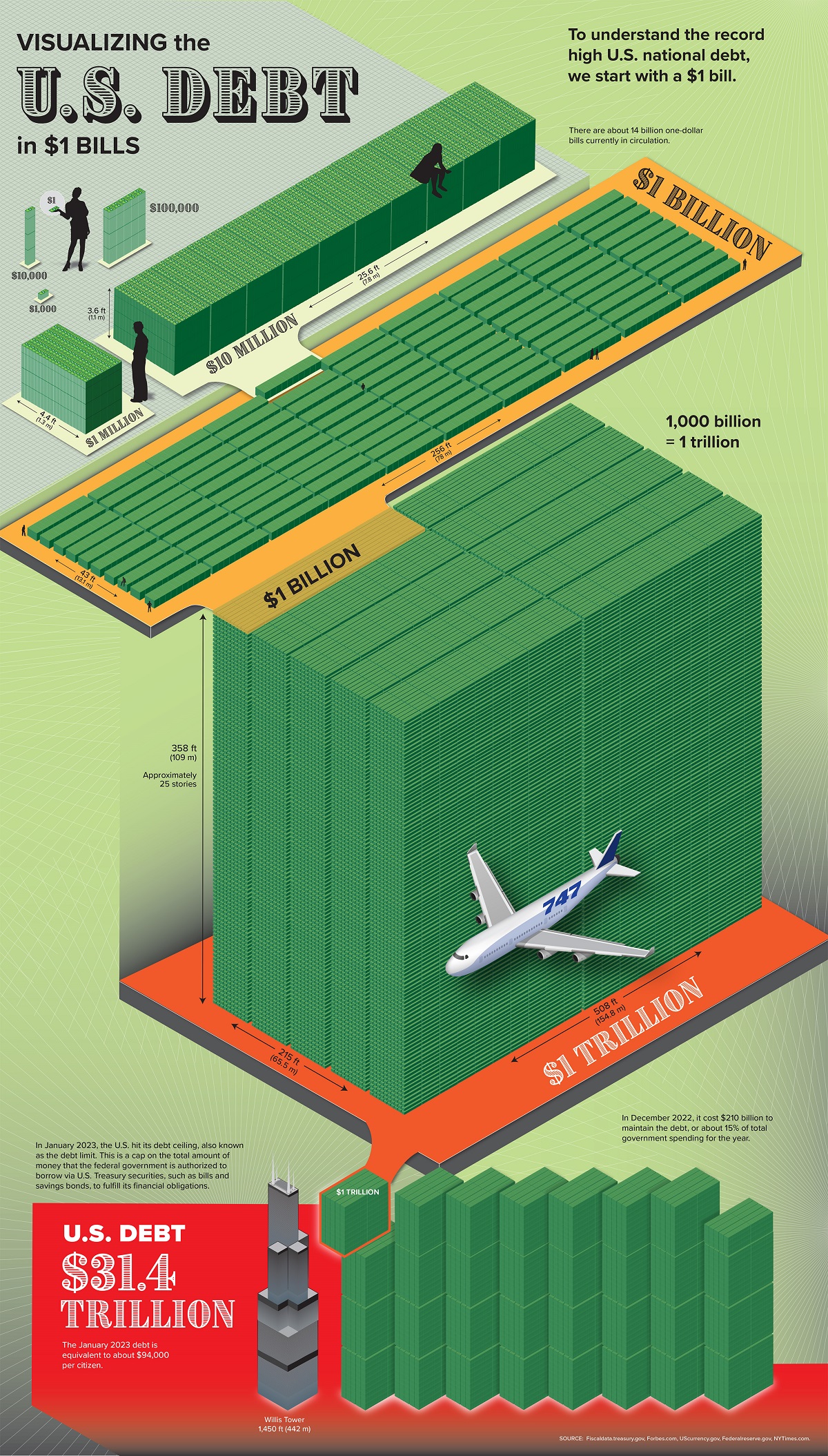
U.S. Debt: Visualizing the $31.4 Trillion Owed in 2023
U.S. Debt: Visualizing the $31.4 Trillion Owed in 2023
Can you picture what $31.4 trillion looks like?
The enormity of U.S. government debt is hard for the average person to wrap their head around. For instance, compared to the median U.S. mortgage, the current level of federal debt is 230 million times larger.
In this graphic, Julie Peasley shows how many one-dollar bills it would take to stack up to the total U.S. debt of $31.4 trillion.
How Did U.S. Debt Get So High?
U.S. national debt is how much money the federal government owes to creditors. When the government spends more than it earns, it has a budget deficit and must issue debt in the form of Treasury securities.
The U.S. has run a deficit for the last 20 years, substantially increasing the national debt. In fact, according to the Department of the Treasury, the current debt is $31.4 trillion.
Stacked up in one-dollar bills, the U.S. debt would be equivalent to almost eight of Chicago’s 110-story Willis Tower.
| Year | Outstanding Debt | Year-Over-Year Increase |
|---|---|---|
| 2023* | $31.4T | 2% |
| 2022 | $30.9T | 9% |
| 2021 | $28.4T | 6% |
| 2020 | $26.9T | 19% |
| 2019 | $22.7T | 6% |
| 2018 | $21.5T | 6% |
| 2017 | $20.2T | 3% |
| 2016 | $19.6T | 8% |
| 2015 | $18.2T | 2% |
| 2014 | $17.8T | 6% |
| 2013 | $16.7T | 4% |
| 2012 | $16.1T | 9% |
| 2011 | $14.8T | 9% |
| 2010 | $13.6T | 14% |
| 2009 | $11.9T | 19% |
| 2008 | $10.0T | 11% |
| 2007 | $9.0T | 6% |
| 2006 | $8.5T | 7% |
| 2005 | $7.9T | 8% |
| 2004 | $7.4T | 9% |
| 2003 | $6.8T | 9% |
| 2002 | $6.2T | 7% |
| 2001 | $5.8T | 2% |
| 2000 | $5.7T | 0% |
Source: Fiscal Data. Debt for 2023 is as of January, with the year-over-year increase reflecting the growth from October 2022 to January 2023. October is the start of the fiscal year for the U.S. government. Debt includes both debt held by the public and intragovernmental holdings.
The last time the government had a surplus was in 2001, when debt rose only 2% due to interest costs. Since then, the largest jumps in U.S. debt have been during the Global Financial Crisis—which saw three straight years of double-digit growth rates—and in 2020 due to trillions of dollars of COVID-19 stimulus.
U.S. federal debt rises during recessions because government revenue, primarily composed of taxes, decreases. At the same time, the government increases spending to help stimulate an economic recovery.
And in today’s case, the U.S. is facing additional financial issues. As the country’s senior population grows and people live longer, this puts pressure on programs that serve older Americans such as Social Security. Healthcare is becoming more expensive and is the second-fastest growing part of the U.S. budget.
The Pros and Cons of Debt
U.S. debt helps fund critical programs for Americans, including retirement and disability benefits, healthcare, economic security, and national defense.
As one example of the impact of these programs, income security nearly halved the percent of the population living below the poverty line in 2019 from 22.8% to 12.2%.
Of course, U.S. debt also comes with challenges. A chief concern is the ability to pay the interest costs on U.S. debt, especially as interest rates rise.
Before rate hikes began, interest costs amounted to 6% of the U.S. budget in the 2021 fiscal year. Fast forward to December 2022, and interest costs amounted to 15% of total government spending since the start of the fiscal year in October.
Addressing the Problem
In January 2023, the U.S. hit its debt ceiling, also known as its borrowing limit. While some countries tie their debt to GDP, the U.S. sets an exact limit in dollar terms.
The government would run out of money to pay its debts this summer if the ceiling is not raised, though policymakers have historically agreed to debt ceiling increases in the past to avoid a default. In 2011, the U.S. narrowly avoided default due to a last-minute debt ceiling negotiation and the country’s credit rating was downgraded as a result.
Tackling U.S. debt is simple in theory: raise taxes or the debt limit, reduce spending, or a combination of all three. However, it’s much more difficult in practice. Which taxes should be raised? Which programs should be cut? What happens the next time the debt limit is reached?

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Markets
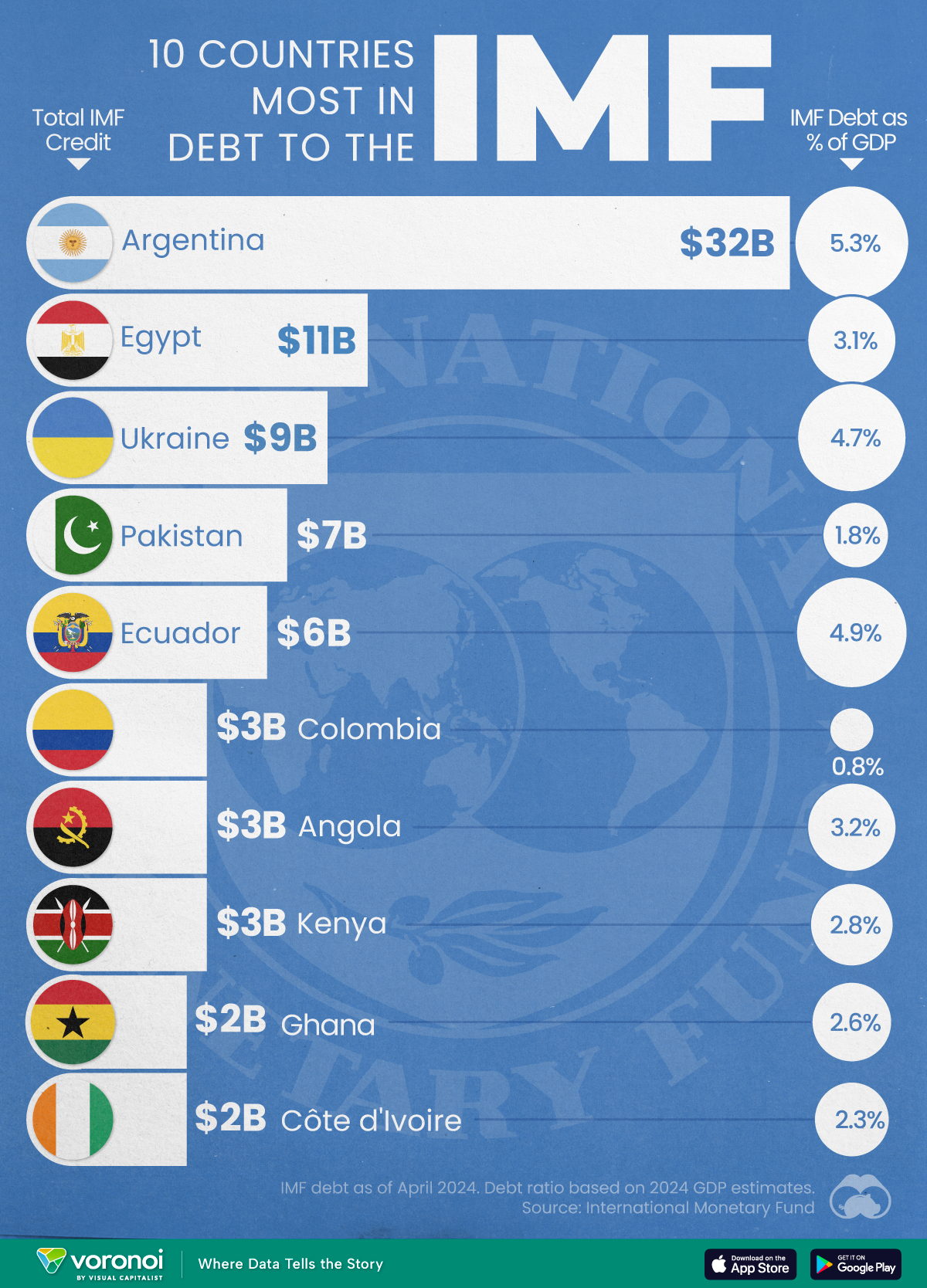
Top 10 Countries Most in Debt to the IMF
Argentina tops the ranking, with a debt equivalent to 5.3% of the country’s GDP.

Top 10 Countries Most in Debt to the IMF
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Established in 1944, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) supports countries’ economic growth by providing financial aid and guidance on policies to enhance stability, productivity, and job opportunities.
Countries seek loans from the IMF to address economic crises, stabilize their currencies, implement structural reforms, and alleviate balance of payments difficulties.
In this graphic, we visualize the 10 countries most indebted to the fund.
Methodology
We compiled this ranking using the International Monetary Fund’s data on Total IMF Credit Outstanding. We selected the latest debt data for each country, accurate as of April 29, 2024.
Argentina Tops the Rank
Argentina’s debt to the IMF is equivalent to 5.3% of the country’s GDP. In total, the country owns more than $32 billion.
| Country | IMF Credit Outstanding ($B) | GDP ($B, 2024) | IMF Debt as % of GDP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇦🇷 Argentina | 32 | 604.3 | 5.3 |
| 🇪🇬 Egypt | 11 | 347.6 | 3.1 |
| 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 9 | 188.9 | 4.7 |
| 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 7 | 374.7 | 1.8 |
| 🇪🇨 Ecuador | 6 | 121.6 | 4.9 |
| 🇨🇴 Colombia | 3 | 386.1 | 0.8 |
| 🇦🇴 Angola | 3 | 92.1 | 3.2 |
| 🇰🇪 Kenya | 3 | 104.0 | 2.8 |
| 🇬🇭 Ghana | 2 | 75.2 | 2.6 |
| 🇨🇮 Ivory Coast | 2 | 86.9 | 2.3 |
A G20 member and major grain exporter, the country’s history of debt trouble dates back to the late 1890s when it defaulted after contracting debts to modernize the capital, Buenos Aires. It has already been bailed out over 20 times in the last six decades by the IMF.
Five of the 10 most indebted countries are in Africa, while three are in South America.
The only European country on our list, Ukraine has relied on international support amidst the conflict with Russia. It is estimated that Russia’s full-scale invasion of the country caused the loss of a third of the country’s economy. The country owes $9 billion to the IMF.
In total, almost 100 countries owe money to the IMF, and the grand total of all of these debts is $111 billion. The above countries (top 10) account for about 69% of these debts.
-

 United States6 days ago
United States6 days agoMapped: Countries Where Recreational Cannabis is Legal
-
 Healthcare2 weeks ago
Healthcare2 weeks agoLife Expectancy by Region (1950-2050F)
-
 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Growth of a $1,000 Equity Investment, by Stock Market
-
 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoMapped: Europe’s GDP Per Capita, by Country
-
 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoCharted: What Frustrates Americans About the Tax System
-
 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoWhere the World’s Aluminum is Smelted, by Country
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State